Air pollution in Europe: High levels of fine particles threaten health
Recent studies indicate that air quality across Europe has seen a noticeable improvement over the last twenty years. However, despite these improvements, a considerable segment of the European populace lives in areas where pollution levels exceed the limits recommended by the World Health Organization (WHO).
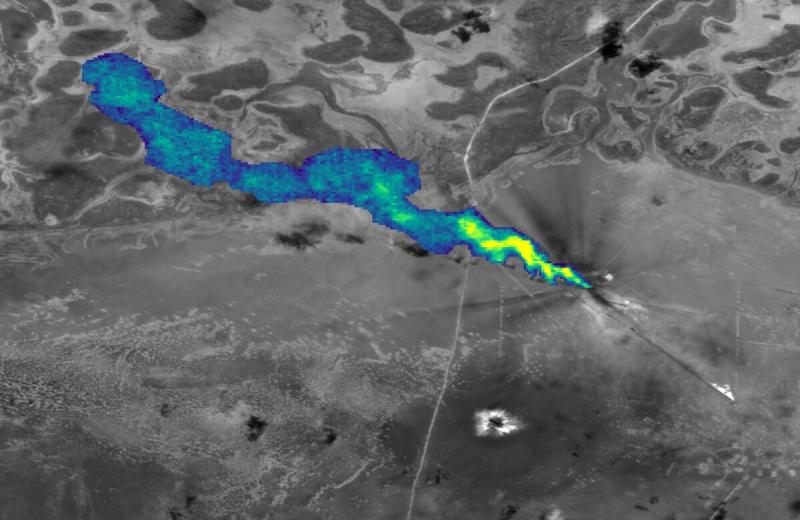
Conducted by researchers at the Institute for Global Health in Barcelona (ISGlobal), a recent study delved into the daily pollution levels across more than 1,400 areas spanning 35 European nations, collectively hosting approximately 543 million individuals. The investigation, spanning from 2003 to 2019, unveiled a decline in the the total levels of suspended particulate matter (PM2.5 and PM10) as well as nitrogen dioxide (NO2) throughout the majority of European regions throughout the past twenty years.
Air quality in Europe has experienced notable improvements, particularly regarding the levels of pollution from pollution caused by coarse particulate matter (PM10) and nitrogen dioxide (NO2), where the largest declines have been observed.
Air pollution still above WHO standards
According to the researchers’ report, despite advancements in air quality, numerous citizens still experience the negative effects of air pollution that exceed the recommended standards of the World Health Organization (WHO).
According to the study, 98% of Europeans continue to live in areas with unfavorable levels of PM2.5. Each year, over tiny particles in the air closely associated with cardiovascular disease , strokes, and diabetes, is linked to approximately 250,000 premature deaths in the European Union each year.

Although the number of deaths caused by PM2.5 fell by 41% from 2005 to 2021, the European Environment Agency encourages member states to continue efforts to further reduce pollution. About 80% of Europeans reside in regions with elevated levels of PM10, and approximately 86% experience high levels of NO2.
Ozone concentrations in southern Europe increased by 0.58%, in other regions of the continent they either remained the same or even decreased. Researcher Zhao-Yue Chen from ISGlobal notes that targeted action is required to address PM2.5 and ozone, especially in light of the increasing risks posed by climate change in Europe.
Study reveals: where are the most polluted areas in Europe?
Air pollution levels have indeed seen a decrease over the past two decades, certain hotspots persist across the continent. The most significant concentrations of particulate matter pollution (PM2.5 and PM10) are notably found in Northern Italy and Eastern Europe. Moreover, Northern Italy and specific regions of Western Europe, such as southern UK, Belgium, and the Netherlands, continue to experience elevated levels of pollution exhibit elevated levels of NO2
The largest decreases in PM2.5 and PM10 concentrations were recorded in central Europe, while NO2 decreased predominantly in metropolitan regions in Western Europe.

A vicious circle: the correlation between climate change and air pollution
Researchers suggest a delicate balance exists between climate change and atmospheric pollution. Elevated temperatures and strong solar radiation play a role in generating ozone through chemical processes. The rise in ozone levels subsequently speeds up the creation of fresh PM2.5 particles. Climate change also heightens the likelihood of wildfires, which further elevate PM2.5 and ozone levels in the air.
“This intricate interaction establishes a hazardous loop, emphasizing the critical importance of addressing the dual challenges posed by climate change and air pollution. concurrently,” remarked Joanne Ballester Claramunt, a research fellow at ISGlobal and the primary author of the study.